zelig-probitgee¶
Generalized Estimating Equation for Probit Regression
The GEE probit estimates the same model as the standard probit regression (appropriate when you have a dichotomous dependent variable and a set of explanatory variables). Unlike in probit regression, GEE probit allows for dependence within clusters, such as in longitudinal data, although its use is not limited to just panel data. The user must first specify a “working” correlation matrix for the clusters, which models the dependence of each observation with other observations in the same cluster. The “working” correlation matrix is a matrix of correlations, where is the size of the largest cluster and the elements of the matrix are correlations between within-cluster observations. The appeal of GEE models is that it gives consistent estimates of the parameters and consistent estimates of the standard errors can be obtained using a robust “sandwich” estimator even if the “working” correlation matrix is incorrectly specified. If the “working” correlation matrix is correctly specified, GEE models will give more efficient estimates of the parameters. GEE models measure population-averaged effects as opposed to cluster-specific effects.
Syntax¶
With reference classes:
z5 <- zprobitgee$new()
z5$zelig(Y ~ X1 + X2, model = "probit.gee",
id = "X3", weights = w, data = mydata)
z5$setx()
z5$sim()
With the Zelig 4 compatibility wrappers:
z.out <- zelig(Y ~ X1 + X2, model = "probit.gee",
id = "X3", weights = w, data = mydata)
x.out <- setx(z.out)
s.out <- sim(z.out, x = x.out)
where id is a variable which identifies the clusters. The data should be sorted by id and should be ordered within each cluster when appropriate.
Additional Inputs¶
Use the following arguments to specify the structure of the “working” correlations within clusters:
- corstr: character string specifying the correlation structure: “independence”, “exchangeable”, “ar1”, “unstructured” and “userdefined”
- See geeglm in package geepack for other function arguments.
Examples¶
Example with Stationary 3 Dependence¶
Attaching the sample turnout dataset:
data(turnout)
Variable identifying clusters
turnout$cluster <- rep(c(1:200), 10)
sorted.turnout <- turnout[order(turnout$cluster), ]
Estimating parameter values:
z.out1 <- zelig(vote ~ race + educate, model = "probit.gee",
id = "cluster", data = sorted.turnout)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## How to cite this model in Zelig:
## Patrick Lam. 2011.
## probit-gee: General Estimating Equation for Probit Regression
## in Christine Choirat, Christopher Gandrud, James Honaker, Kosuke Imai, Gary King, and Olivia Lau,
## "Zelig: Everyone's Statistical Software," http://zeligproject.org/
Summarize estimated paramters:
summary(z.out1)
## Model:
##
## Call:
## z5$zelig(formula = vote ~ race + educate, id = "cluster", data = sorted.turnout)
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std.err Wald Pr(>|W|)
## (Intercept) -0.72595 0.12969 31.3 2.2e-08
## racewhite 0.29908 0.08472 12.5 0.00042
## educate 0.09712 0.00944 105.9 < 2e-16
##
## Estimated Scale Parameters:
## Estimate Std.err
## (Intercept) 0.987 0.0496
##
## Correlation: Structure = independenceNumber of clusters: 200 Maximum cluster size: 10
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
Setting values for the explanatory variables to their default values:
x.out1 <- setx(z.out1)
Simulating quantities of interest:
s.out1 <- sim(z.out1, x = x.out1)
summary(s.out1)
##
## sim x :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 0.771 0.0113 0.772 0.749 0.793
## pv
## 0 1
## [1,] 0.227 0.773
plot(s.out1)
Graphs of Quantities of Interest for Probit GEE Model
Simulating First Differences¶
Estimating the risk difference (and risk ratio) between low education (25th percentile) and high education (75th percentile) while all the other variables held at their default values.
x.high <- setx(z.out1, educate = quantile(turnout$educate, prob = 0.75))
x.low <- setx(z.out1, educate = quantile(turnout$educate, prob = 0.25))
s.out2 <- sim(z.out1, x = x.high, x1 = x.low)
summary(s.out2)
##
## sim x :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 0.825 0.0105 0.825 0.804 0.845
## pv
## 0 1
## [1,] 0.181 0.819
##
## sim x1 :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 0.707 0.0146 0.706 0.678 0.734
## pv
## 0 1
## [1,] 0.285 0.715
## fd
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] -0.118 0.0121 -0.118 -0.141 -0.0939
plot(s.out2)
Graphs of Quantities of Interest for Probit GEE Model
Example with Fixed Correlation Structure¶
User-defined correlation structure
corr.mat <- matrix(rep(0.5, 100), nrow = 10, ncol = 10)
diag(corr.mat) <- 1
corr.mat <- fixed2Zcor(corr.mat, id = sorted.turnout$cluster,
waves = sorted.turnout$race)
Generating empirical estimates:
z.out2 <- zelig(vote ~ race + educate, model = "probit.gee",
id = "cluster", data = sorted.turnout,
corstr = "fixed", zcor = corr.mat)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## How to cite this model in Zelig:
## Patrick Lam. 2011.
## probit-gee: General Estimating Equation for Probit Regression
## in Christine Choirat, Christopher Gandrud, James Honaker, Kosuke Imai, Gary King, and Olivia Lau,
## "Zelig: Everyone's Statistical Software," http://zeligproject.org/
Viewing the regression output:
summary(z.out2)
The Model¶
Suppose we have a panel dataset, with denoting the binary
dependent variable for unit 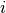 at time .
is a vector or cluster of correlated data where is
correlated with for some or all
. Note that the model assumes correlations within
at time .
is a vector or cluster of correlated data where is
correlated with for some or all
. Note that the model assumes correlations within
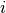 but independence across
but independence across 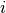 .
.
The stochastic component is given by the joint and marginal distributions
where and are unspecified distributions with means and . GEE models make no distributional assumptions and only require three specifications: a mean function, a variance function, and a correlation structure.
The systematic component is the mean function, given by:
where is the cumulative distribution function of the Normal distribution with mean 0 and unit variance, is the vector of explanatory variables for unit
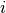 at time and
at time and 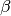 is the vector of coefficients.
is the vector of coefficients.The variance function is given by:
The correlation structure is defined by a “working” correlation matrix, where is the size of the largest cluster. Users must specify the structure of the “working” correlation matrix a priori. The “working” correlation matrix then enters the variance term for each
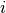 , given by:
, given by:where is a diagonal matrix with the variance function as the th diagonal element, is the “working” correlation matrix, and is a scale parameter. The parameters are then estimated via a quasi-likelihood approach.
In GEE models, if the mean is correctly specified, but the variance and correlation structure are incorrectly specified, then GEE models provide consistent estimates of the parameters and thus the mean function as well, while consistent estimates of the standard errors can be obtained via a robust “sandwich” estimator. Similarly, if the mean and variance are correctly specified but the correlation structure is incorrectly specified, the parameters can be estimated consistently and the standard errors can be estimated consistently with the sandwich estimator. If all three are specified correctly, then the estimates of the parameters are more efficient.
The robust “sandwich” estimator gives consistent estimates of the standard errors when the correlations are specified incorrectly only if the number of units
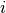 is relatively large and the number
of repeated periods is relatively small. Otherwise, one
should use the “naïve” model-based standard errors, which assume that
the specified correlations are close approximations to the true
underlying correlations. See for more details.
is relatively large and the number
of repeated periods is relatively small. Otherwise, one
should use the “naïve” model-based standard errors, which assume that
the specified correlations are close approximations to the true
underlying correlations. See for more details.
Quantities of Interest¶
All quantities of interest are for marginal means rather than joint means.
The method of bootstrapping generally should not be used in GEE models. If you must bootstrap, bootstrapping should be done within clusters, which is not currently supported in Zelig. For conditional prediction models, data should be matched within clusters.
The expected values (qi$ev) for the GEE probit model are simulations of the predicted probability of a success:
given draws of
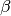 from its sampling distribution, where
is a vector of values, one for each independent
variable, chosen by the user.
from its sampling distribution, where
is a vector of values, one for each independent
variable, chosen by the user.The first difference (qi$fd) for the GEE probit model is defined as
The risk ratio (qi$rr) is defined as
In conditional prediction models, the average expected treatment effect (att.ev) for the treatment group is
where is a binary explanatory variable defining the treatment () and control () groups. Variation in the simulations are due to uncertainty in simulating , the counterfactual expected value of for observations in the treatment group, under the assumption that everything stays the same except that the treatment indicator is switched to .
Output Values¶
The output of each Zelig command contains useful information which you may view. For examle, if you run z.out <- zelig(y ~ x, model = probit.gee, id, data), then you may examine the available information in z.out by using names(z.out), see the coefficients by using z.out$coefficients, and a default summary of information through summary(z.out). Other elements available through the $ operator are listed below.
- From the zelig() output object z.out, you may extract:
- coefficients: parameter estimates for the explanatory variables.
- residuals: the working residuals in the final iteration of the fit.
- fitted.values: the vector of fitted values for the systemic component, .
- linear.predictors: the vector of
- max.id: the size of the largest cluster.
- From summary(z.out), you may extract:
- coefficients: the parameter estimates with their associated standard errors, -values, and -statistics.
- working.correlation: the “working” correlation matrix
- From the sim() output object s.out, you may extract quantities of
interest arranged as matrices indexed by simulation
x-observation (for more than one x-observation). Available quantities
are:
- qi$ev: the simulated expected probabilities for the specified values of x.
- qi$fd: the simulated first difference in the expected probabilities for the values specified in x and x1.
- qi$rr: the simulated risk ratio for the expected probabilities simulated from x and x1.
- qi$att.ev: the simulated average expected treatment effect for the treated from conditional prediction models.
See also:¶
The geeglm function is part of the geepack package by Søren Højsgaard, Ulrich Halekoh and Jun Yan. Advanced users may wish to refer to help(geepack) and help(family).
Højsgaard S, Halekoh U and Yan J (2006). “The R Package geepack for Generalized Estimating Equations.” Journal of Statistical Software, 15/2, pp. 1-11.
Yan J and Fine JP (2004). “Estimating Equations for Association Structures.” Statistics in Medicine, 23, pp. 859-880.
Yan J (2002). “geepack: Yet Another Package for Generalized Estimating Equations.” R-News, 2/3, pp. 12-14.