zeliggam-logitgam¶
Generalized Additive Model for Dichotomous Dependent Variables
This function runs a nonparametric Generalized Additive Model (GAM) for dichotomous dependent variables.
Syntax¶
With reference classes:
z5 <- zlogitgam$new()
z5$zelig(y ~ x1 + s(x2), data = mydata)
z5$setx()
z5$sim()
With the Zelig 4 compatibility wrappers:
z.out <- zelig(y ~ x1 + s(x2), model = "logit.gam", data = mydata)
x.out <- setx(z.out)
s.out <- sim(z.out, x = x.out)
where s() indicates a variable to be estimated via nonparametric smooth. All variables for which s() is not specified, are estimated via standard parametric methods.
Additional Inputs¶
In addition to the standard inputs, zelig() takes the following additional options for GAM models.
- method: Controls the fitting method to be used. Fitting
methods are selected via a list environment within method = gam.method(). See gam.method() for details.
- scale: Generalized Cross Validation (GCV) is used if
scale = 0 (see the “Model” section for details) except for Logit models where a Un-Biased Risk Estimator (UBRE) (also see the “Model” section for details) is used with a scale parameter assumed to be 1. If scale is greater than 1, it is assumed to be the scale parameter/variance and UBRE is used. If scale is negative GCV is used.
knots: An optional list of knot values to be used for the construction of basis functions.
H: A user supplied fixed quadratic penalty on the parameters of the GAM can be supplied with this as its coefficient matrix. For example, ridge penalties can be added to the parameters of the GAM to aid in identification on the scale of the linear predictor.
sp: A vector of smoothing parameters for each term.
...: additional options passed to the logit.gam model. See the mgcv library for details.
Examples¶
Basic Example¶
Create some count data:
set.seed(0)
n <- 100
sig <- 2
x0 <- runif(n, 0, 1)
x1 <- runif(n, 0, 1)
x2 <- runif(n, 0, 1)
x3 <- runif(n, 0, 1)
f0 <- function(x) 2 * sin(pi * x)
f1 <- function(x) exp(2 * x)
f2 <- function(x) 0.2 * x ^ 11 * (10 * (1 - x)) ^ 6 + 10 * (10 * x) ^ 3 * (1 - x) ^ 10
f2 <- function(x) 0 * x
f <- f0(x0) + f1(x1) + f2(x2)
g <- (f - 5) / 3
g <- binomial()$linkinv(g)
y <- rbinom(g,1,g)
my.data <- as.data.frame(cbind(y, x0, x1, x2, x3))
Estimate the model, summarize the results, and plot nonlinearities:
z.out <- zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), model = "logit.gam", data = my.data)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## Error in zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), model = "logit.gam", : Model 'logit.gam' not found
summary(z.out)
## Model:
##
## Formula: cbind(dem, rep, non) ~ cbind(black, white, natam)
## Total sims:
## Burnin discarded:
## Sims saved:
##
##
## Acceptance ratios for Beta (averaged over units):
## dem rep
## black 0.467 0.394
## white 0.313 0.285
## natam 0.593 0.522
##
## Acceptance ratios for alpha:
## columns
## rows dem rep non
## black 0.683 0.192 0.144
## white 0.702 0.552 0.388
## natam 0.629 0.203 0.156
##
## Draws for Alpha:
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 4.9606 0.8259 3.6629 7.0602
## white.dem 6.9323 0.4460 6.1259 7.8585
## natam.dem 5.9738 1.1092 3.6357 7.8956
## black.rep 0.6211 0.0873 0.4562 0.8134
## white.rep 4.1032 0.2658 3.5925 4.5817
## natam.rep 0.6134 0.0897 0.4676 0.8301
## black.non 0.4989 0.0810 0.3727 0.6651
## white.non 2.1443 0.1392 1.9154 2.4543
## natam.non 0.6025 0.0891 0.4654 0.7921
##
## Aggregate cell counts (summed over units):
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 66542 1155 64360 68005
## white.dem 124692 1332 122913 127083
## natam.dem 25112 192 24683 25404
## black.rep 6733 547 6117 7862
## white.rep 94161 670 92712 95146
## natam.rep 1240 118 1020 1476
## black.non 4971 801 3792 6347
## white.non 41682 889 40120 43024
## natam.non 1156 169 840 1482
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
plot(z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]], pages = 1, residuals = TRUE)
## Error in xy.coords(x, y, xlabel, ylabel, log): 'x' is a list, but does not have components 'x' and 'y'
Note that the plot() function can be used after model estimation and before simulation to view the nonlinear relationships in the independent variaables.
Set values for the explanatory variables to their default (mean/mode) values, then simulate, summarize and plot quantities of interest:
x.out <- setx(z.out)
## Error in cbind(black, white, natam): object 'black' not found
s.out <- sim(z.out, x = x.out)
## Error in sim(z.out, x = x.out): object 'x.out' not found
summary(s.out)
## Error in summary(s.out): object 's.out' not found
plot(s.out)
## Error in plot(s.out): object 's.out' not found
Simulating First Differences¶
Estimating the risk difference (and risk ratio) between low values (20th percentile) and high values (80th percentile) of the explanatory variable x3 while all the other variables are held at their default (mean/mode) values.
x.high <- setx(z.out, x3 = quantile(my.data$x3, 0.8))
## Error: Variable 'x3' not in data set.
x.low <- setx(z.out, x3 = quantile(my.data$x3, 0.2))
## Error: Variable 'x3' not in data set.
s.out <- sim(z.out, x = x.high, x1 = x.low)
summary(s.out)
##
## sim x :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 0.0617 0.0463 0.0502 0.00839 0.184
## 2 0.4409 0.1632 0.4142 0.18592 0.805
## 3 0.2777 0.0870 0.2743 0.12117 0.461
## 4 0.2197 0.1571 0.2071 0.00317 0.551
## pv
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 2.64 0.879 2 1 4
##
## sim x1 :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 0.5437 0.0707 0.54502 4.00e-01 0.675
## 2 0.3853 0.0554 0.38683 2.78e-01 0.489
## 3 0.0482 0.0401 0.03907 3.71e-04 0.137
## 4 0.0227 0.0401 0.00514 1.16e-07 0.145
## pv
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 1.54 0.681 1 1 3
## fd
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 0.4821 0.0893 0.4897 0.287 0.63438
## 2 -0.0556 0.1619 -0.0213 -0.445 0.18646
## 3 -0.2295 0.1026 -0.2321 -0.441 -0.03889
## 4 -0.1970 0.1317 -0.1959 -0.467 -0.00317
plot(s.out)
Zeliggam-logitgam2
Variations in GAM model specification¶
Note that setx and sim work as shown in the above examples for any GAM model. As such, in the interest of parsimony, I will not re-specify the simulations of quantities of interest. An extra ridge penalty (useful with convergence problems):
z.out <- zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), H = diag(0.5, 37), model = "logit.gam", data = my.data)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## Error in zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), H = diag(0.5, 37), model = "logit.gam", : Model 'logit.gam' not found
summary(z.out)
## Model:
##
## Formula: cbind(dem, rep, non) ~ cbind(black, white, natam)
## Total sims:
## Burnin discarded:
## Sims saved:
##
##
## Acceptance ratios for Beta (averaged over units):
## dem rep
## black 0.467 0.394
## white 0.313 0.285
## natam 0.593 0.522
##
## Acceptance ratios for alpha:
## columns
## rows dem rep non
## black 0.683 0.192 0.144
## white 0.702 0.552 0.388
## natam 0.629 0.203 0.156
##
## Draws for Alpha:
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 4.9606 0.8259 3.6629 7.0602
## white.dem 6.9323 0.4460 6.1259 7.8585
## natam.dem 5.9738 1.1092 3.6357 7.8956
## black.rep 0.6211 0.0873 0.4562 0.8134
## white.rep 4.1032 0.2658 3.5925 4.5817
## natam.rep 0.6134 0.0897 0.4676 0.8301
## black.non 0.4989 0.0810 0.3727 0.6651
## white.non 2.1443 0.1392 1.9154 2.4543
## natam.non 0.6025 0.0891 0.4654 0.7921
##
## Aggregate cell counts (summed over units):
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 66542 1155 64360 68005
## white.dem 124692 1332 122913 127083
## natam.dem 25112 192 24683 25404
## black.rep 6733 547 6117 7862
## white.rep 94161 670 92712 95146
## natam.rep 1240 118 1020 1476
## black.non 4971 801 3792 6347
## white.non 41682 889 40120 43024
## natam.non 1156 169 840 1482
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
plot(z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]], pages = 1, residuals = TRUE)
## Error in xy.coords(x, y, xlabel, ylabel, log): 'x' is a list, but does not have components 'x' and 'y'
Set the smoothing parameter for the first term, estimate the rest:
z.out <- zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), sp = c(0.01, -1, -1, -1), model = "logit.gam", data = my.data)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## Error in zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), sp = c(0.01, -1, -1, : Model 'logit.gam' not found
summary(z.out)
## Model:
##
## Formula: cbind(dem, rep, non) ~ cbind(black, white, natam)
## Total sims:
## Burnin discarded:
## Sims saved:
##
##
## Acceptance ratios for Beta (averaged over units):
## dem rep
## black 0.467 0.394
## white 0.313 0.285
## natam 0.593 0.522
##
## Acceptance ratios for alpha:
## columns
## rows dem rep non
## black 0.683 0.192 0.144
## white 0.702 0.552 0.388
## natam 0.629 0.203 0.156
##
## Draws for Alpha:
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 4.9606 0.8259 3.6629 7.0602
## white.dem 6.9323 0.4460 6.1259 7.8585
## natam.dem 5.9738 1.1092 3.6357 7.8956
## black.rep 0.6211 0.0873 0.4562 0.8134
## white.rep 4.1032 0.2658 3.5925 4.5817
## natam.rep 0.6134 0.0897 0.4676 0.8301
## black.non 0.4989 0.0810 0.3727 0.6651
## white.non 2.1443 0.1392 1.9154 2.4543
## natam.non 0.6025 0.0891 0.4654 0.7921
##
## Aggregate cell counts (summed over units):
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 66542 1155 64360 68005
## white.dem 124692 1332 122913 127083
## natam.dem 25112 192 24683 25404
## black.rep 6733 547 6117 7862
## white.rep 94161 670 92712 95146
## natam.rep 1240 118 1020 1476
## black.non 4971 801 3792 6347
## white.non 41682 889 40120 43024
## natam.non 1156 169 840 1482
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
plot(z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]], pages = 1, residuals = TRUE)
## Error in xy.coords(x, y, xlabel, ylabel, log): 'x' is a list, but does not have components 'x' and 'y'
Set lower bounds on smoothing parameters:
z.out <- zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), min.sp = c(0.001, + 0.01, 0, 10), model = "logit.gam", data = my.data)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## Error in zelig(y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3), min.sp = c(0.001, +0.01, : Model 'logit.gam' not found
summary(z.out)
## Model:
##
## Formula: cbind(dem, rep, non) ~ cbind(black, white, natam)
## Total sims:
## Burnin discarded:
## Sims saved:
##
##
## Acceptance ratios for Beta (averaged over units):
## dem rep
## black 0.467 0.394
## white 0.313 0.285
## natam 0.593 0.522
##
## Acceptance ratios for alpha:
## columns
## rows dem rep non
## black 0.683 0.192 0.144
## white 0.702 0.552 0.388
## natam 0.629 0.203 0.156
##
## Draws for Alpha:
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 4.9606 0.8259 3.6629 7.0602
## white.dem 6.9323 0.4460 6.1259 7.8585
## natam.dem 5.9738 1.1092 3.6357 7.8956
## black.rep 0.6211 0.0873 0.4562 0.8134
## white.rep 4.1032 0.2658 3.5925 4.5817
## natam.rep 0.6134 0.0897 0.4676 0.8301
## black.non 0.4989 0.0810 0.3727 0.6651
## white.non 2.1443 0.1392 1.9154 2.4543
## natam.non 0.6025 0.0891 0.4654 0.7921
##
## Aggregate cell counts (summed over units):
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 66542 1155 64360 68005
## white.dem 124692 1332 122913 127083
## natam.dem 25112 192 24683 25404
## black.rep 6733 547 6117 7862
## white.rep 94161 670 92712 95146
## natam.rep 1240 118 1020 1476
## black.non 4971 801 3792 6347
## white.non 41682 889 40120 43024
## natam.non 1156 169 840 1482
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
plot(z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]], pages = 1)
## Error in xy.coords(x, y, xlabel, ylabel, log): 'x' is a list, but does not have components 'x' and 'y'
A GAM with 3df regression spline term & 2 penalized terms:
z.out <- zelig(y ~ s(x0, k = 4, fx = TRUE, bs = "tp") + s(x1, k = 12) + s(x2, k = 15), model = "logit.gam", data = my.data)
## Warning in readLines(zeligmixedmodels): incomplete final line found on
## '/usr/lib64/R/library/ZeligMultilevel/JSON/zelig5mixedmodels.json'
## Error in zelig(y ~ s(x0, k = 4, fx = TRUE, bs = "tp") + s(x1, k = 12) + : Model 'logit.gam' not found
summary(z.out)
## Model:
##
## Formula: cbind(dem, rep, non) ~ cbind(black, white, natam)
## Total sims:
## Burnin discarded:
## Sims saved:
##
##
## Acceptance ratios for Beta (averaged over units):
## dem rep
## black 0.467 0.394
## white 0.313 0.285
## natam 0.593 0.522
##
## Acceptance ratios for alpha:
## columns
## rows dem rep non
## black 0.683 0.192 0.144
## white 0.702 0.552 0.388
## natam 0.629 0.203 0.156
##
## Draws for Alpha:
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 4.9606 0.8259 3.6629 7.0602
## white.dem 6.9323 0.4460 6.1259 7.8585
## natam.dem 5.9738 1.1092 3.6357 7.8956
## black.rep 0.6211 0.0873 0.4562 0.8134
## white.rep 4.1032 0.2658 3.5925 4.5817
## natam.rep 0.6134 0.0897 0.4676 0.8301
## black.non 0.4989 0.0810 0.3727 0.6651
## white.non 2.1443 0.1392 1.9154 2.4543
## natam.non 0.6025 0.0891 0.4654 0.7921
##
## Aggregate cell counts (summed over units):
## Mean Std. Error 2.5% 97.5%
## black.dem 66542 1155 64360 68005
## white.dem 124692 1332 122913 127083
## natam.dem 25112 192 24683 25404
## black.rep 6733 547 6117 7862
## white.rep 94161 670 92712 95146
## natam.rep 1240 118 1020 1476
## black.non 4971 801 3792 6347
## white.non 41682 889 40120 43024
## natam.non 1156 169 840 1482
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
plot(z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]], pages = 1)
## Error in xy.coords(x, y, xlabel, ylabel, log): 'x' is a list, but does not have components 'x' and 'y'
The Model¶
GAM models use families the same way GLM models do: they specify the
distribution and link function to use in model fitting. In the case of
logit.gam a logistic link function is used. Specifically,
let be the binary dependent variable for observation 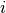 which
takes the value of either 0 or 1.
which
takes the value of either 0 or 1.
The stochastic component is given by the joint and marginal distributions
where .
The systematic component is given by:
- where is the vector of covariates,
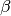 is the vector of
is the vector of coefficients and for is the set of smooth terms.
- where is the vector of covariates,
Generalized additive models (GAMs) are similar in many respects to generalized linear models (GLMs). Specifically, GAMs are generally fit by penalized maximum likelihood estimation and GAMs have (or can have) a parametric component identical to that of a GLM. The difference is that GAMs also include in their linear predictors a specified sum of smooth functions.
In this GAM implementation, smooth functions are represented using penalized regression splines. Two techniques may be used to estimate smoothing parameters: Generalized Cross Validation (GCV),
or an Un-Biased Risk Estimator (UBRE) (which is effectively just a rescaled AIC),
where is the deviance, is the number of observations, is the scale parameter, and is the effective degrees of freedom of the model. The use of GCV or UBRE can be set by the user with the scale command described in the “Additional Inputs” section and in either case, smoothing parameters are chosen to minimize the GCV or UBRE score for the model.
Estimation for GAM models proceeds as follows: first, basis functions and a set (one or more) of quadratic penalty coefficient matrices are constructed for each smooth term. Second, a model matrix is obtained for the parametric component of the GAM. These matrices are combined to produce a complete model matrix and a set of penalty matrices for the smooth terms. Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares (IRLS) is then used to estimate the model; at each iteration of the IRLS, a penalized weighted least squares model is run and the smoothing parameters of that model are estimated by GCV or UBRE. This process is repeated until convergence is achieved.
Further details of the GAM fitting process are given in Wood (2000, 2004, 2006).
Quantities of Interest¶
The quantities of interest for the logit.gam model are the same as those for the standard logistic regression.
The expected value (qi$ev) for the logit.gam model is the mean of simulations from the stochastic component,
The predicted values (qi$pr) are draws from the Binomial distribution with mean equal to the simulated expected value .
The first difference (qi$fd) for the logit.gam model is defined as
for .
Output Values¶
The output of each Zelig command contains useful information which you may view. For example, if you run z.out <- zelig(y ~ x, model = "logit.gam", data), then you may examine the available information in z.out by using names(z.out), see the coefficients by using coefficients(z.out), and a default summary of information through summary(z.out). Other elements available through the $ operator are listed below.
- From the zelig() output stored in z.out$zelig.out$z.out[[1]],
you may extract:
- coefficients: parameter estimates for the explanatory variables.
- fitted.values: the vector of fitted values for the explanatory variables.
- residuals: the working residuals in the final iteration of the IRLS fit.
- linear.predictors: the vector of .
- aic: Akaike’s Information Criterion (minus twice the maximized log-likelihood plus twice the number of coefficients).
- method: the fitting method used.
- converged: logical indicating weather the model converged or not.
- smooth: information about the smoothed parameters.
- df.residual: the residual degrees of freedom.
- df.null: the residual degrees of freedom for the null model.
- data: the input data frame.
- model: the model matrix used.
- From summary(z.out) (as well as from
zelig()), you may extract:
- p.coeff: the coefficients of the parametric components of the model.
- se: the standard errors of the entire model.
- p.table: the coefficients, standard errors, and associated statistics for the parametric portion of the model.
- s.table: the table of estimated degrees of freedom, estimated rank, statistics, and values for the nonparametric portion of the model.
- cov.scaled: a matrix of scaled covariances.
- cov.unscaled: a matrix of unscaled covariances.
- From the sim() output stored in s.out, you
may extract:
- qi$ev: the simulated expected probabilities for the specified values of x.
- qi$pr: the simulated predicted values for the specified values of x.
- qi$fd: the simulated first differences in the expected probabilities simulated from x and x1.
See also¶
The logit.gam model is adapted from the mgcv package by Simon N. Wood. Advanced users may wish to refer to help(gam), and other documentation accompanying the mgcv package. All examples are reproduced and extended from mgcv‘s gam() help pages.
## Error in eval(expr, envir, enclos): object 'zlogitgam' not found
Rosen O, Jiang W, King G and Tanner M (2001). “Bayesian and Frequentist Inference for Ecological Inference: The R x C case.” Statistica Neerlandia, 167, pp. 134-156.
Lau O, Moore RT and Kellermann M (2012). eiPack: eiPack: Ecological Inference and Higher-Dimension Data Management. R package version 0.1-7, <URL: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=eiPack>.